
RESOURCES & TIPS
Help and More
In our eyes, a successful project is one that keeps safety and well-being of oneself and others in mind. In our industry, machinery and equipment is always evolving, becoming evermore efficient and powerful, and with it more complex and confusing! Concrete Engineers Malaysia is here to help. Our online Training resources will help you and your workers learn to be more proficient and safe at work. We hope you will find this free tool useful and inspiring.

WHAT IS CONCRETE MIX DESIGN
Concrete is a material made of cement/cementitious materials, water, and aggregates.
It has been used for many years in Earth’s history as a building material for structures such as bridges, houses, dams, highways, sidewalks, and skyscrapers.
Concrete has several properties such as strength and durability and can be cast into any shape, form, and texture, and be coloured for aesthetics.
Unfortunately, there are some challenges still faced today in delivering uniform and high-quality concrete products, and therefore, concrete technologies continue to be developed to modify and improve both properties of fresh and hardened concrete.
Concrete mix design is the process of selecting suitable ingredients of concrete and determine the relative proportions to produce concrete with certain performance and durability requirements.
Different concrete mix designs with different materials, even with the same proportions, can have significantly different properties of strength and durability.
The properties of concrete can also be affected through production, placement, finishing, and curing practices. It is therefore important that concrete mixes are designed, produced, placed, cured, and tested by competent individuals.
Hence, concrete mix design is the process of finding right proportions of cement, sand and aggregates for concrete to achieve target strength in structures.
So, concrete mix design can be stated as Concrete Mix = Cement: Sand: Aggregates.
The concrete mix design involves various steps, calculations, and laboratory testing to find right mix proportions.
This process is usually adopted for structures which requires higher grades of concrete such as M25 and above and large construction projects where quantity of concrete consumption is huge.
Benefits of concrete mix design is that it provides the right proportions of materials, thus making the concrete construction economical in achieving required strength of structural members.
As, the quantity of concrete required for large constructions are huge, economy in quantity of materials such as cement makes the project construction economical.

HOW TO ENSURE CONCRETE QUALITY
When supplying major construction projects, it is essential that thorough and accurate concrete testing is carried out to meet client requirements and ensure safety.
With a wide variety of quarried materials used as aggregates in concrete, a combination of properties can be achieved to meet the requirements of a specific application.
To ensure that the mix meets these specifications, in addition to testing the aggregate for properties including particle size, shape and texture, density, and chemical resistance, it is vital that the concrete incorporating the aggregate is tested thoroughly and accurately.
The latest generation of sample testing technology is allowing concrete to be tested considerably more efficiently and reliably than has previously been possible, helping to realize sound structures, improve long-term safety and reduce costs.
Concrete is generally chosen for construction projects due to its combination of strength and versatility; however, with this flexibility come important issues that must also be addressed.
Despite thorough knowledge of the aggregate used, the nature of other materials and of production processes, it is unlikely that any two batches will be identical in their qualities.
Mixing methods can, for example, vary from batch to batch, or supplier to supplier, potentially resulting in finished precast components or liquid mixes with an unacceptable level of variance.
Stringent quality-control processes are essential when using both fresh concrete for pouring and spraying (shotcrete), and precast components such as liners and lintels, as the implications for inadequate quality checks can be fatal.
In addition to the need to ensure the health and safety of construction workers, there are considerable commercial and legal repercussions, with the potential costs associated with court action, compensation, and repairs, as well as the potential for negative publicity.
Furthermore, the life of a structure can be significantly reduced as a result of incorrect formulation or consistency in mixing.

CONCRETE TESTING
WHEN DO I NEED CONCRETE TESTING AND WHAT IS IT?
Due to its importance in structural engineering, concrete is often required to bear and support heavy loads.
Therefore, it needs to be tested before you use it to make sure it’s of sufficient strength and durability.
Different types of Concrete Testing can be carried out depending on whether the concrete is freshly mixed or hardened and can range from testing its carbonation depth or bond strength to testing for water permeability/moisture absorption.
Concrete Testing – meeting the standards
In the UK all concrete is required to meet British Standards (BSI) before it can be used.
Material concrete testing to find out the exact components of the concrete can be carried out in a laboratory to ensure that it contains exactly what the manufacturer claims it does, whilst on site testing can also be carried out to ensure that the mix is fit for purpose.
Reputable companies will often use third parties to test their concrete in order to make sure that any results are neutral.
Types of Concrete Testing
Slump Testing:
The most common type of concrete testing on-site is a slump test.
This is carried out to ensure that the concrete is workable after it has been mixed and that the correct amount of water has been added.
It is almost always conducted by the supervisor on site and involves filling a slump cone with three equal layers of concrete before turning it upside down to see whether the concrete stays in place.
In order for the concrete to be considered usable, it has to form a true slump. In other words, the concrete has to maintain more or less the same shape.
If the concrete has subsided slightly then it is considered a shear slump and will have to be re-mixed.
If it collapses completely then it is deemed to be a collapse slump.
Compression Testing:
Compression testing is a laboratory test carried out to measure the strength and durability of the concrete.
A sample batch of the concrete is measured out in cubic moulds of around 150mm x 150mm x 15 mm (or 100mm x100mm x100mm).
Usually, a minimum of 3 cubes are taken from each sample which are then stored at set temperatures, depending on when the cube is to be tested.
If the cube is set to be tested in more than 7 days it should be stored at 15 – 25 dc, if tested in less than 7 days, it should be stored at 18 – 22 dc.
The concrete sample is then put into a compression testing machine which subjects the concrete to a required amount of force in order to measure the extent of how much it cracks.

WHAT ARE THE EXAMPLES OF THE USE OF NANOTECHNOLOGY IN CONCRETE TECHNOLOGY?
Nanoparticles are used in concrete for various reasons. The most important one is to increase concrete mechanical properties, such as its compressive strength.
Nano-materials like Nano-silica, Carbon Nanotubes by filling nanopores in concrete and preventing the spread of cracks, respectively, increase the strength of concrete.
There are lots of published articles in this regard.
There are mixes of nanosilica or silica gel with mortar in order to improve mechanical properties such as compactness.
It can also be used as nanomodification to modify the cement properties using nanoporous thin film coating (NPTF).

WHICH TYPE OF SUPERPLASTICIZER PROVIDES THE BEST DISPERSION OF NANO-SILICA IN WATER FOR CONCRETE PREPARATION?
There are many chemical admixtures (superplasticizers) use to modify the properties of fresh concrete.
The best approach is to perform a test using various types of superplasticizer and select the best one.
An empirical selection is not always efficient.
The best superplasticizer is the one that can handle hydration processes under nano scale. In many cases capillaries filled with nano particles without any water reaching possibility. The best superplasticizer must be manufactured to overcome this problem specifically!. Then all nano materials react with Ca(OH)2.
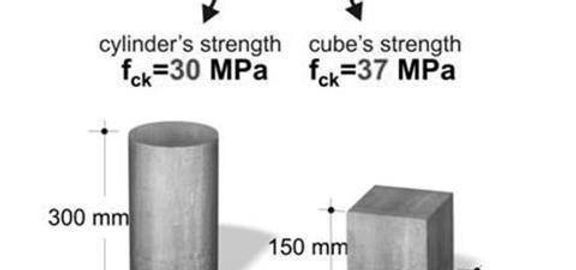
WHAT IS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CONCRETE STRENGTH MEASURED USING CUBES AND CYLINDERS?
Concrete strength measured using concrete cubes produce a results different than concrete cylinders.
Conservative estimates put concrete cylinders at 80% of concrete cubes, for high-strength concrete some say the percentage is near 100%.
You can normalize cube strength with cylindrical.
Strength is eventually the stress which is inversely related to cross-sectional area.
Extensive research is present on the relation of compressive strength with the size of specimen and strength class.
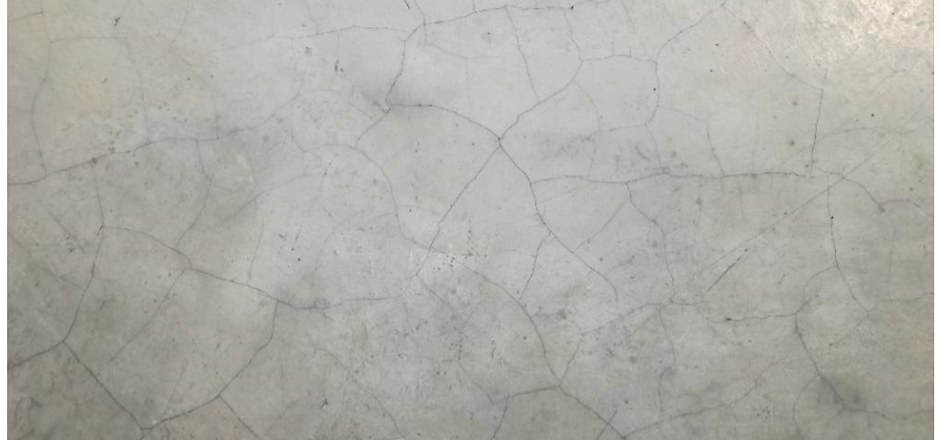

WHY DOES CONCRETE CRACK AT EARLY STAGES WITHOUT ANY LOAD?
Cracking at early age is mainly due to internal temperature (and humidity sometimes) gradients induced by the processes of setting and curing of concrete.
Temperature and water content distributions across the concrete section depends also of the structure boundary conditions and on the environment.
Appropriate curing and mixture design (limiting heat generation during setting) may mitigate the risk of cracking.






